The Best Fluffy Pancakes recipe you will fall in love with. Full of tips and tricks to help you make the best pancakes.
25 Types of Nursing Specialties: Exploring the Diversity of Nursing

Nursing is a vital profession within the healthcare system, with nurses playing a crucial role in patient care, advocacy, and health promotion. While many people are familiar with the general concept of nursing, it is important to recognize the vast array of specialized nursing roles that exist. This blog aims to provide an in-depth exploration of the different types of nursing specialties, highlighting their unique roles, responsibilities, and contributions to healthcare.
25 Types of Nursing Specialties: Exploring the Diversity of Nursing
1. Pediatric Nursing:
Pediatric nurses are experts in providing care for newborns, kids, and teenagers. They possess the necessary expertise to identify and cater to the special physical, emotional, and developmental requirements of young patients.
Education: Obtain a nursing degree (diploma, ADN, or BSN), pass the NCLEX-RN exam, and gain experience. Additional certifications like Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) or Certified Pediatric Nurse (CPN) may be required by some facilities.
Roles and Responsibilities: Provide complete care to newborns, kids, and teenagers. Responsibilities may include assessing growth and development, administering pediatric medications, supporting families, and addressing the unique physical and emotional needs of pediatric patients.
2. Geriatric Nursing:

Geriatric nurses focus on the care of elderly patients, addressing age-related health issues, promoting healthy aging, managing chronic conditions, and providing support for end-of-life care.
Education: A diploma, ADN, or BSN in nursing, passing the NCLEX-RN test, and accumulating experience are all requirements. Specialized certifications like Geriatric Nursing Certification (RN-BC) are available.
Roles and Responsibilities: Focusing on the healthcare needs of elderly patients. Responsibilities may include managing chronic conditions, promoting functional independence, addressing geriatric syndromes, and providing end-of-life care.
3. Critical Care Nursing:
Critical care nurses work in intensive care units (ICUs) or other essential settings of care, providing specialized care to patients with life-threatening conditions or those requiring close monitoring and advanced medical interventions.
Education: Nursing degree (diploma, ADN, or BSN), passing the NCLEX-RN exam, and gaining experience. Additional certifications like Critical Care Registered Nurses (CCRN) are standard.
Roles and Responsibilities: Providing intensive care units (ICUs) or other critical care environments with specialized treatment for critically sick patients. Responsibilities may include monitoring vital signs, administering complex treatments, managing life support equipment, and collaborating with the healthcare team.
4. Emergency Nursing:
Emergency nurses work in emergency departments (EDs) and are responsible for assessing, triaging, and providing urgent care to patients with acute injuries or illnesses that require immediate medical attention.
Education: Nursing degree (diploma, ADN, or BSN), passing the NCLEX-RN exam, and gaining experience. Certification options include Certified Emergency Nurse (CEN).
Roles and Responsibilities: Assessing, triaging, and providing urgent care to patients in emergency departments. Responsibilities include rapid assessment, administering emergency treatments, collaborating with the healthcare team, and crisis management.
5. Psychiatric Nursing:
Psychiatric nurses treat patients with psychiatric problems and are experts in mental health. They assess, diagnose, and provide treatment, counseling, and support to individuals of all ages experiencing mental health challenges.
Education: Nursing degree (diploma, ADN, or BSN), passing the NCLEX-RN exam, and gaining experience. Advanced certifications like Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing (RN-BC) are available.
Roles and Responsibilities: Providing medical attention to those with mental problems. Responsibilities may include performing mental health assessments, administering medications, implementing therapeutic interventions, and advocating for patients’ mental health needs.
6. Oncology Nursing:
Oncology nurses focus on caring for patients with cancer. They provide support, administer treatments such as chemotherapy, manage side effects, and educate patients and families about the disease and treatment options.
Education: Nursing degree (diploma, ADN, or BSN), passing the NCLEX-RN exam, and gaining experience. Certifications like Oncology Certified Nurse (OCN) are standard.
Roles and Responsibilities: Specializing in caring for patients with cancer. Chemotherapy administration, cancer-related symptom management, emotional support, and treatment choices education are among the responsibilities.
7. Cardiac Nursing:
Cardiac nurses specialize in the care of patients with heart conditions, such as heart disease, congestive heart failure, or those recovering from cardiac procedures. They monitor patients, administer medications, provide education, and assist with cardiac rehabilitation.
Education: Nursing degree (diploma, ADN, or BSN), passing the NCLEX-RN exam, and gaining experience. Advanced certifications like Cardiac-Vascular Nursing (RN-BC) are available.
Roles and Responsibilities: Focusing on patients with cardiac conditions. Responsibilities may include monitoring cardiac health, administering medications, assisting with procedures like cardiac catheterization, and providing patient education on lifestyle modifications.
8. Neonatal Nursing:
Newborn babies are cared for by neonatal nurses, especially those who were born prematurely or had medical issues. They offer specialized care, which includes keeping track of vital signs, dispensing medications, and assisting neonatal families.
Education: Nursing degree (diploma, ADN, or BSN), passing the NCLEX-RN exam, and gaining experience. Additional certifications like Neonatal Resuscitation Program (NRP) and Neonatal Intensive Care Nursing (RNC-NIC) are standard.
Roles and Responsibilities: Providing specialized care to newborn infants, particularly premature or ill babies. Responsibilities include monitoring vital signs, administering neonatal medications, supporting breastfeeding, and educating parents about neonatal care.
9. Perioperative Nursing:
From preoperative planning to aftercare, perioperative nurses provide assistance throughout surgical procedures. They work along with the surgical team, guarantee patient security, and offer patients and families’ emotional support.
Education: Nursing degree (diploma, ADN, or BSN), passing the NCLEX-RN exam, and gaining experience. Advanced certifications like Certified Perioperative Nurses (CNOR) are available.
Roles and Responsibilities: Assisting surgeons and patients during surgical procedures. Responsibilities may include preparing patients for surgery, monitoring vital signs during the procedure, managing surgical instruments and equipment, and providing post-operative care and education.
10. Rehabilitation Nursing:

Rehabilitation nurses assist patients in recovering from diseases, impairments, or injuries. They develop and implement personalized care plans, facilitate therapy sessions, and educate patients on managing their conditions.
Education: Nursing degree (diploma, ADN, or BSN), passing the NCLEX-RN exam, and gaining experience. Advanced certifications like Certified Rehabilitation Registered Nurse (CRRN) are available.
Roles and Responsibilities: Focusing on assisting patients in recovering from injuries, disabilities, or chronic illnesses. Responsibilities may include developing and implementing rehabilitation plans, facilitating therapies, providing emotional support, and promoting independence.
11. Community Health Nursing:
Rehabilitation nurses help patients recover from injuries, illnesses, or disabilities. They develop and implement personalized care plans, facilitate therapy sessions, and educate patients on managing their conditions.
Education: Nursing degree (diploma, ADN, or BSN), passing the NCLEX-RN exam, and gaining experience. Certifications like Public Health Nursing (PHN) may be pursued.
Roles and Responsibilities: Working within communities to promote health and provide preventive care. Responsibilities may include conducting health assessments, offering health education and counseling, coordinating community resources, and advocating for public health initiatives.
12. School Nursing:
School nurses provide healthcare services and support to students within educational institutions. They address acute and chronic health issues, administer medications, and promote health and wellness within the school community.
Education: Nursing degree (diploma, ADN, or BSN), passing the NCLEX-RN exam, and gaining experience. Some states require additional certification or specialized training in school nursing.
Roles and Responsibilities: Providing healthcare services and support within educational institutions. Responsibilities may include managing student health records, administering medications, conducting health screenings, and responding to medical emergencies.
13. Forensic Nursing:
Forensic nurses combine nursing knowledge with forensic science to care for victims of violence or abuse. They collect evidence, document injuries, offer crisis intervention, and collaborate with legal authorities.
Education: Nursing degree (diploma, ADN, or BSN), passing the NCLEX-RN exam, and gaining experience. Advanced certifications like Sexual Assault Nurse Examiner (SANE) are available.
Roles and Responsibilities: Combining nursing and legal knowledge to provide care for victims of violence or abuse. Responsibilities may include performing forensic examinations, collecting evidence, providing crisis intervention, and collaborating with law enforcement and legal authorities.
14. Nephrology Nursing:
The treatment of patients with renal illnesses or those undergoing dialysis is their area of expertise as nephrology nurses. They manage dialysis treatments, monitor patients’ fluid and electrolyte balance, and educate patients on kidney health.
Education: Nursing degree (diploma, ADN, or BSN), passing the NCLEX-RN exam, and gaining experience. Certifications like Certified Nephrology Nurse (CNN) or Certified Dialysis Nurse (CDN) are standard.
Roles and Responsibilities: Focusing on treating patients with renal problems or those undergoing dialysis. Responsibilities may include assessing kidney function, managing dialysis treatments, administering medications, and educating patients about kidney health.
15. Palliative Care Nursing:
The primary goals of palliative care nurses are to soothe patients with serious diseases or those getting end-of-life care and control their discomfort and provide them with emotional support. They strive to improve patients’ and families’ quality of life.
Education: Nursing degree (diploma, ADN, or BSN), passing the NCLEX-RN exam, and gaining experience. Advanced certifications like Hospice and Palliative Nurse (HPNA) are available.
Roles and Responsibilities: Concentrating on offering support and comfort to people with terminal diseases. Responsibilities include managing pain and symptoms, facilitating end-of-life discussions, providing emotional support to patients and their families, and coordinating care across healthcare settings.
16. Diabetes Nursing:
Diabetes nurses are experts at managing and caring for patients with diabetes. They educate patients about diabetes self-management, monitor blood sugar levels, administer insulin, and support patients in maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Education: Nursing degree (diploma, ADN, or BSN), passing the NCLEX-RN exam, and gaining experience. Certifications like Certified Diabetes Care and Education Specialist (CDCES) are standard.
Roles and Responsibilities: Specializing in the treatment and management of diabetic patients. Responsibilities may include educating patients on diabetes self-care, monitoring blood glucose levels, administering insulin, and collaborating with the healthcare team to develop comprehensive care plans.
17. Infectious Disease Nursing:
Infectious disease nurses focus on preventing, managing, and treating infectious diseases. They educate patients and the community about infection control measures, administer medications and collaborate with other healthcare professionals to contain outbreaks.
Education: Nursing degree (diploma, ADN, or BSN), passing the NCLEX-RN exam, and gaining experience. Certifications like Certification in Infection Control (CIC) or Advanced Public Health Nursing (APHN-BC) are available.
Roles and Responsibilities: Focusing on infectious illness management, prevention, and treatment. Responsibilities may include infection control practices, educating patients and communities on disease prevention, implementing vaccination programs, and collaborating with infectious disease specialists.
18. Occupational Health Nursing:
Occupational health professionals enhance the well-being and safety of workers at work. They assess workplace hazards, provide health screenings, promote preventive measures, and offer support for occupational injuries or illnesses.
Education: Nursing degree (diploma, ADN, or BSN), passing the NCLEX-RN exam, and gaining experience. Additional certifications like Certified Occupational Health Nurse (COHN) are standard.
Roles and Responsibilities: Putting emphasis on workplace employee health and safety. Responsibilities may include conducting health assessments, promoting occupational health and safety practices, managing workers’ compensation cases, and providing health education and counseling.
19. Public Health Nursing:
Public health nurses work to promote and improve the health of communities and populations. They focus on preventive care, health education, disease surveillance, and community health promotion initiatives.
Education: Nursing degree (diploma, ADN, or BSN), passing the NCLEX-RN exam, and gaining experience. Certifications like Public Health Nursing (PHN) may be pursued.
Roles and Responsibilities: Working to enhance and promote population and community health. Responsibilities may include disease prevention and control, health promotion and education, conducting community health assessments, and advocating for public health policies.
20. Informatics Nursing:
Informatics nurses combine nursing expertise with information technology to improve patient care outcomes. They manage and analyze healthcare data, implement electronic health record systems, and support the use of technology in healthcare delivery.
Education: Nursing degree (diploma, ADN, or BSN), passing the NCLEX-RN exam, and gaining experience. Advanced certifications like Informatics Nursing (RN-BC) are available.
Roles and Responsibilities: Using information technology and nursing knowledge to enhance patient care. Responsibilities may include managing electronic health records, optimizing clinical information systems, analyzing healthcare data, and facilitating communication between healthcare professionals.
21. Wound Care Nursing:
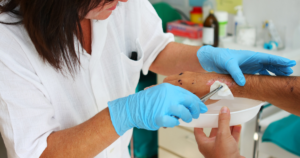
Wound care nurses are experts in managing and treating a variety of wound forms. They assess wounds, develop care plans, provide wound dressings, and educate patients on wound healing and prevention of complications.
Education: Nursing degree (diploma, ADN, or BSN), passing the NCLEX-RN exam, and gaining experience. Certifications like Certified Wound Care Nurse (CWCN) or Wound, Ostomy, and Continence Nurse (WOCN) are common.
Roles and Responsibilities: Specializing in the care and healing of a variety of wounds. Responsibilities may include assessing and documenting wound status, implementing appropriate wound care interventions, educating patients on wound healing, and collaborating with wound care specialists.
22. Radiology Nursing:
Radiology nurses work in radiology departments and assist with diagnostic imaging procedures such as X-rays, ultrasounds, and MRIs. They ensure patient safety, provide pre-and post-procedure care, and assist radiologists during procedures.
Education: Nursing degree (diploma, ADN, or BSN), passing the NCLEX-RN exam, and gaining experience. Additional certifications or training in radiology nursing may be beneficial.
Roles and Responsibilities: Providing care for patients undergoing diagnostic imaging procedures. Responsibilities may include preparing patients for radiology exams, administering contrast agents, monitoring patients during procedures, and ensuring radiation safety protocols are followed.
23. Flight Nursing:
Flight nurses provide medical care and transportation to critically ill or injured patients during air transport or evacuation. They stabilize patients, administer medications, and provide emergency care during the flight.
Education: Nursing degree (diploma, ADN, or BSN), passing the NCLEX-RN exam, gaining experience, and completing specialized training or certification as a flight nurse.
Roles and Responsibilities: Delivering medical care to patients during air transport or evacuation. Responsibilities include providing emergency care in flight, managing critical patients, collaborating with the flight crew and healthcare team, and ensuring patient safety during transport.
24. Nurse Educator:
Nurse educators play a vital role in nursing education by teaching and mentoring future nurses. They develop curricula, facilitate learning experiences, assess student progress, and provide guidance and support to aspiring nurses.
Education: Nursing degree (diploma, ADN, or BSN), passing the NCLEX-RN exam, gaining experience, and completing advanced education like a Master of Science in Nursing (MSN) or a Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP).
Roles and Responsibilities: Educating and training future nurses in academic or clinical settings. Responsibilities may include developing curriculum, teaching nursing courses, mentoring and supervising students, conducting research, and staying updated on nursing best practices.
25. Obstetric and Gynecological Nursing:
Obstetric and gynecological nursing, also known as OB/GYN nursing, is a specialized area of nursing that focuses on providing care to women during pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period, as well as addressing various gynecological health concerns. OB/GYN nurses play a crucial role in supporting women through all stages of their reproductive health.
Education: Nursing degree (diploma, ADN, or BSN), passing the NCLEX-RN exam, and gaining experience. Advanced certifications like Inpatient Obstetric Nursing (RNC-OB) or Women’s Health Care Nurse Practitioner (WHNP-BC) can be pursued for specialized roles.
Roles and Responsibilities: Providing gynecological care and caring for women during pregnancy, delivery, and the postpartum period. Responsibilities may include conducting prenatal assessments, assisting with labor and delivery, providing postpartum care, performing gynecological exams, educating patients on reproductive health, and assisting with family planning.
References:




